In recent decades, most African countries have increased the availability of sexual and reproductive health care, yet many people still lack access to these essential services. This fact sheet presents evidence as of 2019 on the need for, impact of and cost of fully investing in treatment for the major curable STIs among women aged 15–49 in 53 African Union member states.
This fact sheet underscores the recommendations made in Article 43 of the Addis Ababa Declaration on Population and Development in Africa Beyond 2014, which commits member states to taking certain concerted actions. Those include providing affordable and accurate rapid diagnostic tests for HIV, other STIs and reproductive tract infections, as well as information, education and treatment for all women and men.
Unmet need for services
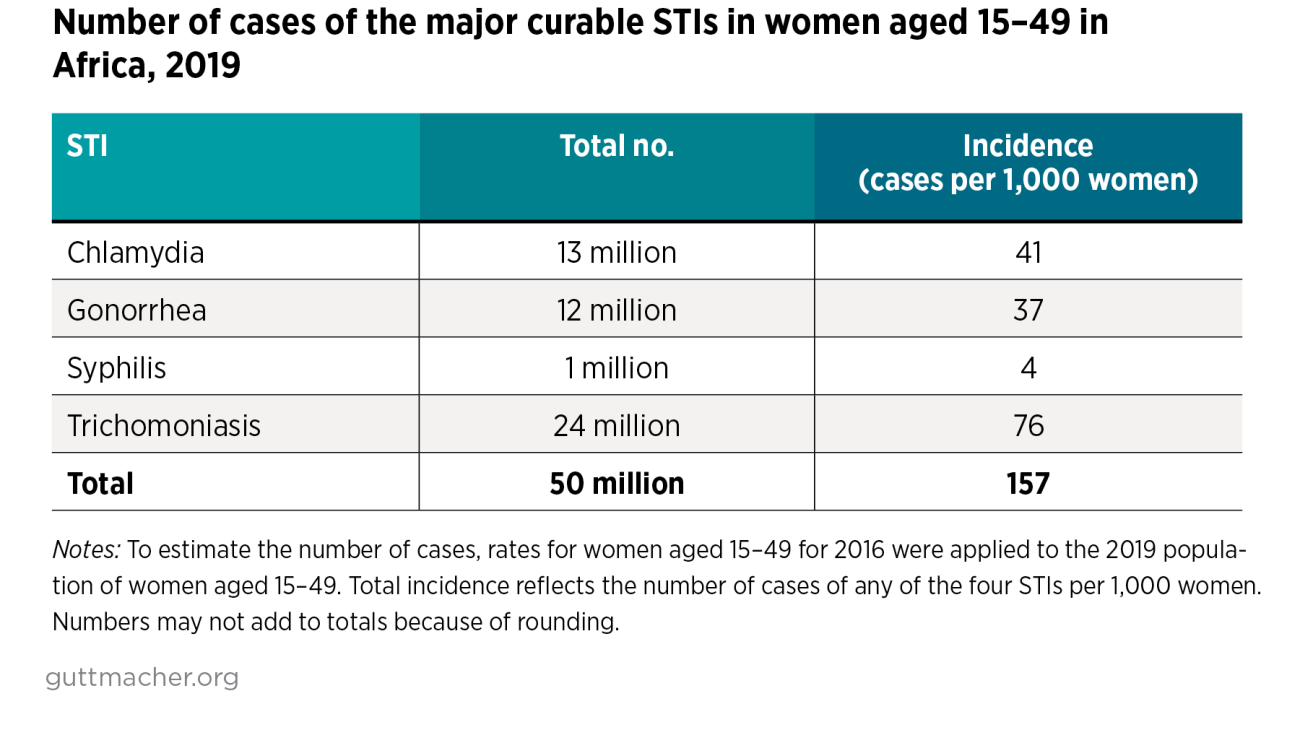
- Approximately 50 million women aged 15–49 in Africa become infected annually with one of the four major curable STIs: chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis and trichomoniasis.
- Forty-two million (85%) do not receive treatment, often because they do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected.
- More than eight million cases of pelvic inflammatory disease occur annually as a result of untreated chlamydia and gonorrhea, and more than one million of these cases result in infertility.